New to Voyager? Please start here.
Issue Let’s Encrypt certificate using Azure DNS
This tutorial shows how to issue free SSL certificate from Let’s Encrypt via DNS challenge for domains using Azure DNS service.
This article has been tested with a GKE cluster.
$ kubectl version --short
Client Version: v1.8.8
Server Version: v1.8.8-gke.0
1. Setup Issuer
Go to your DNS Zone page:
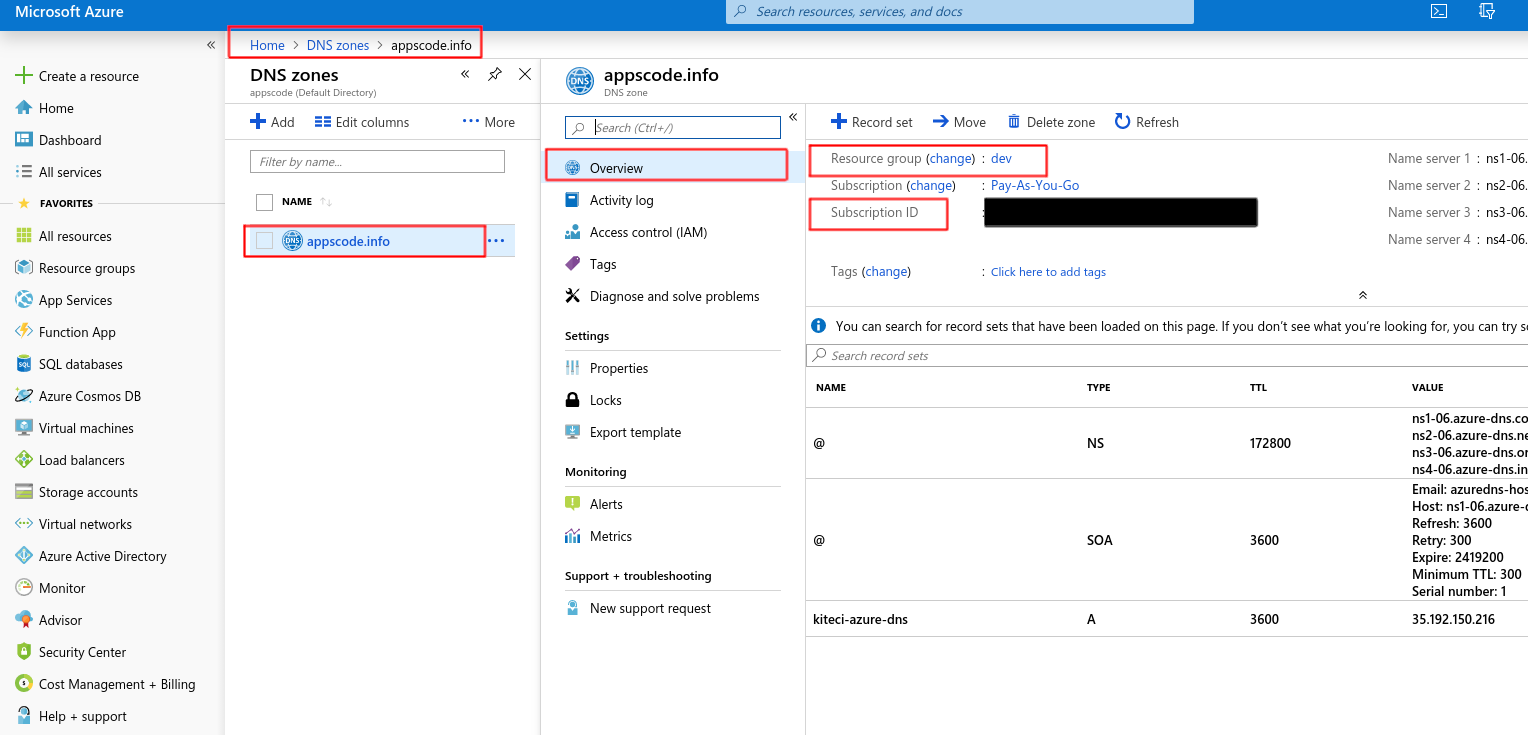
You’ll need this Subscription id and Resource group later while creating issuer.
Go to Azure Active Directory -> App registrations and click on New Registration
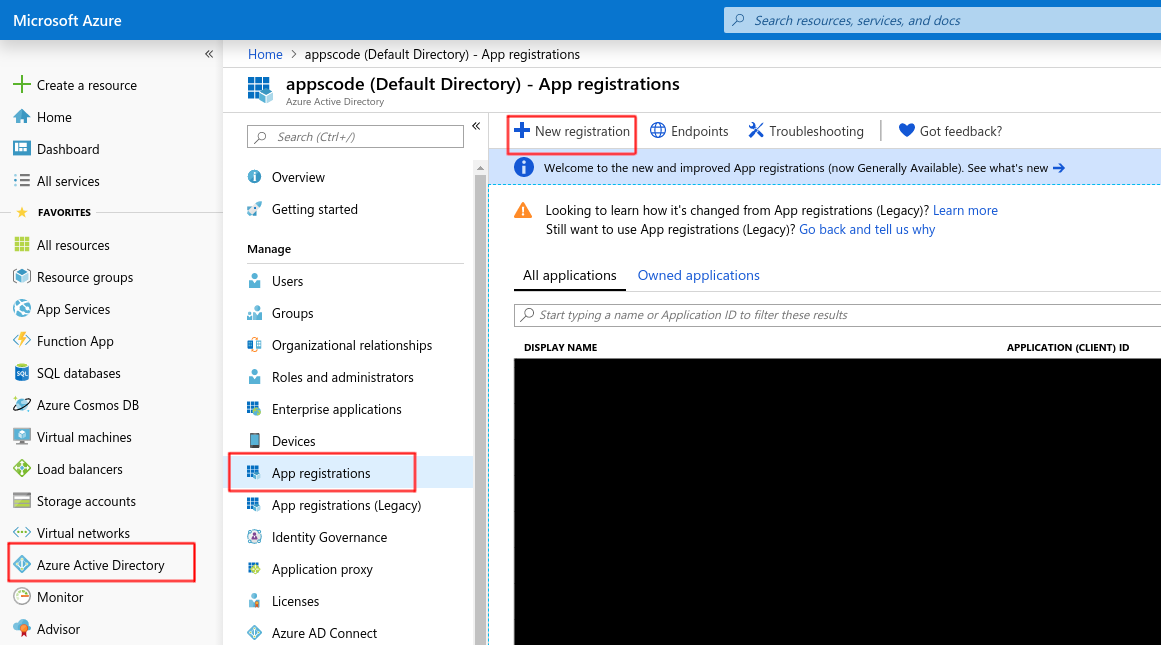
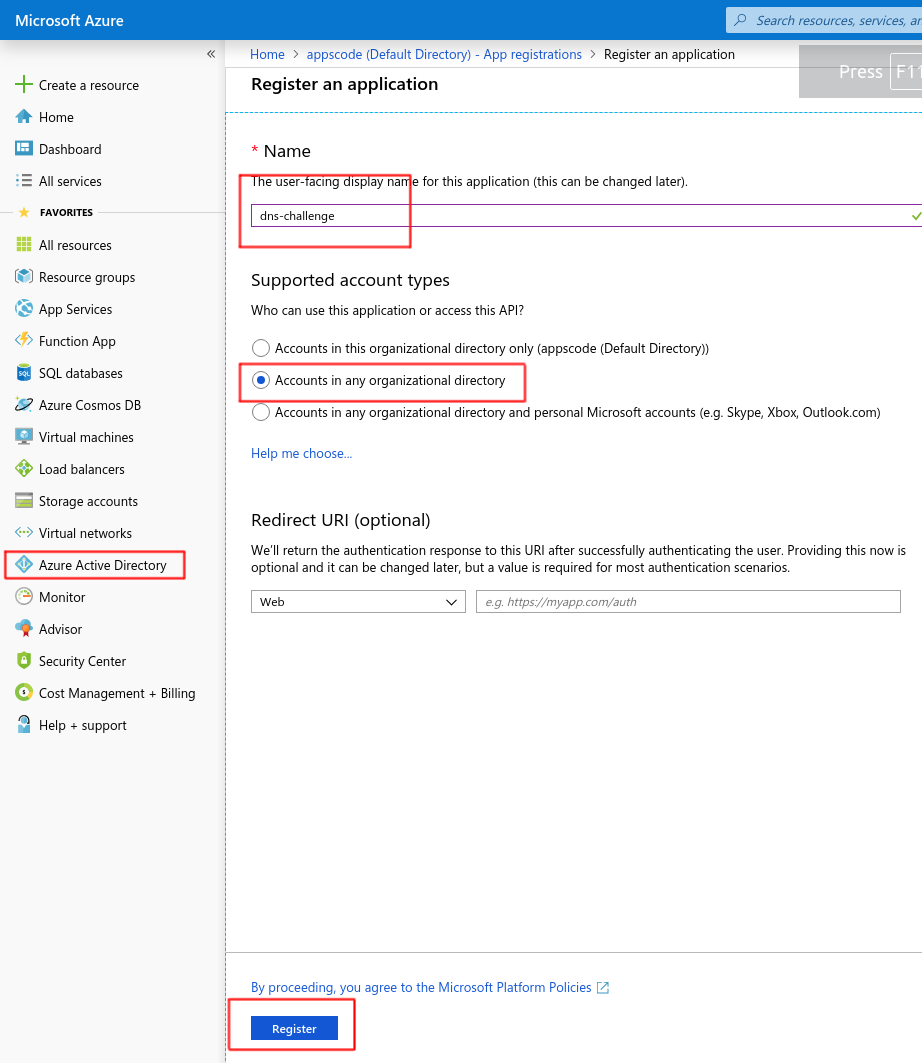
You’ll need the Application (client) ID and Directory (tenant) ID later for creating issuer.
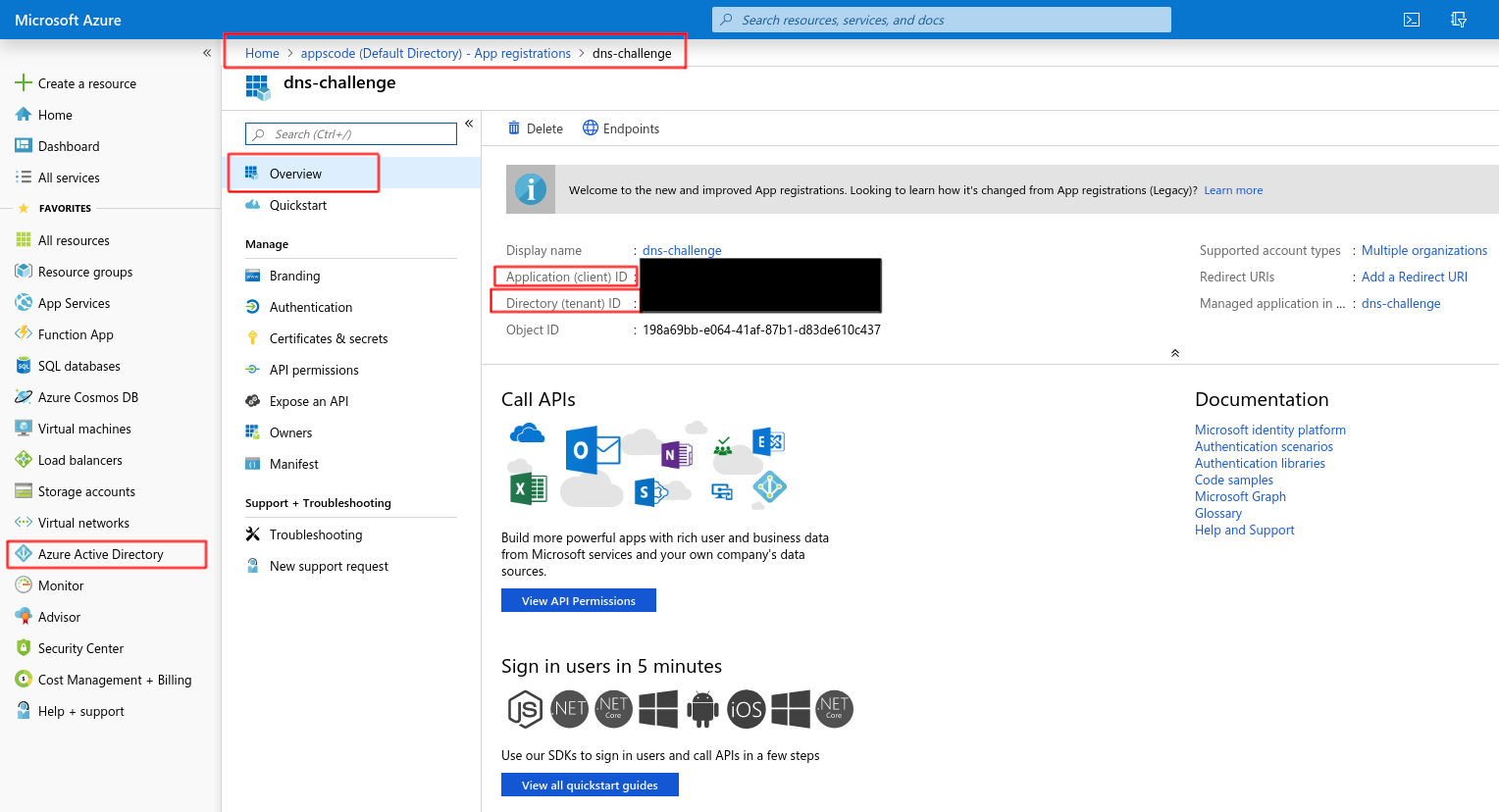
Now, create a new client-secret.
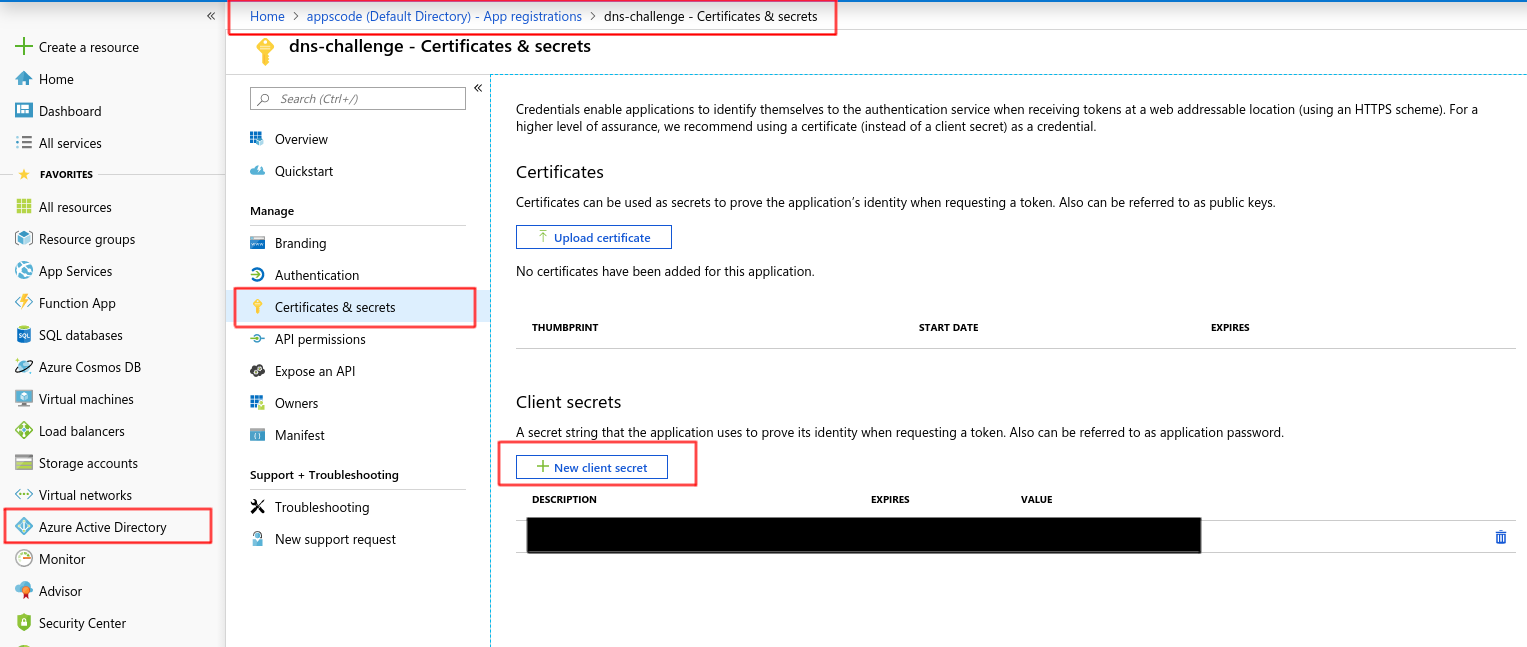
Copy the password for this client-secret and create a kubernetes secret:
kubectl create secret generic azuredns-secret --from-literal=client-secret="sdfsdfTEser@k3casdfbsdfsdf_m[4"
Now go to Subscriptions page and click on the corresponding subscription for your dns zone:
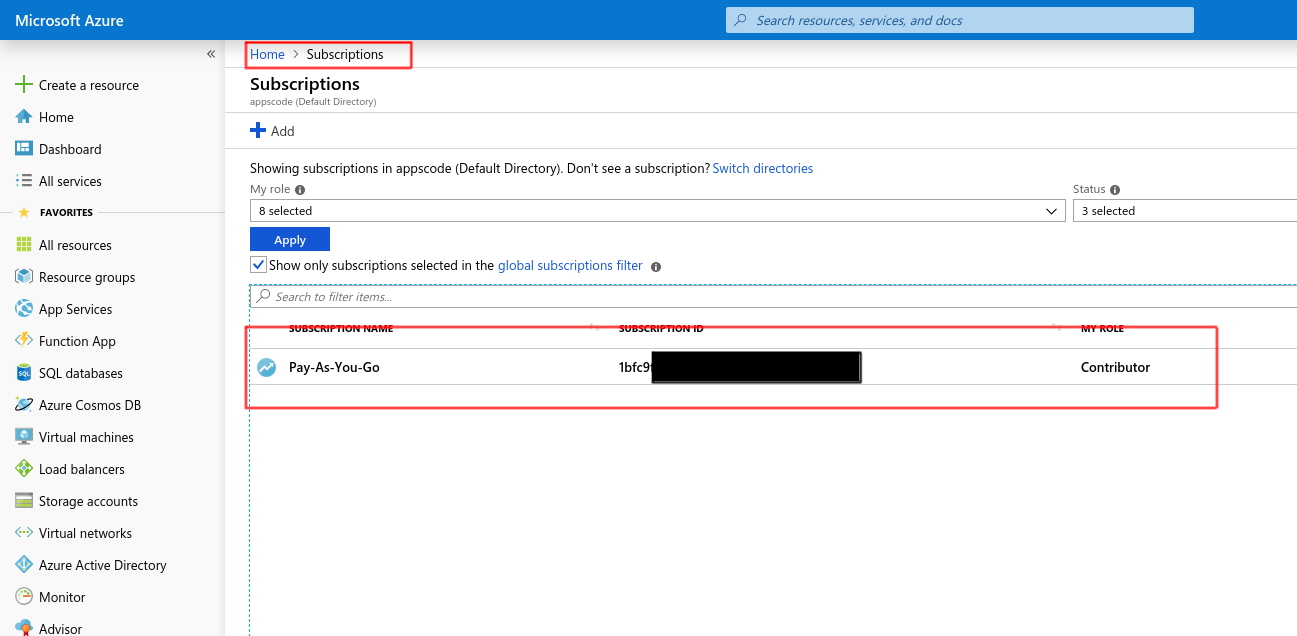
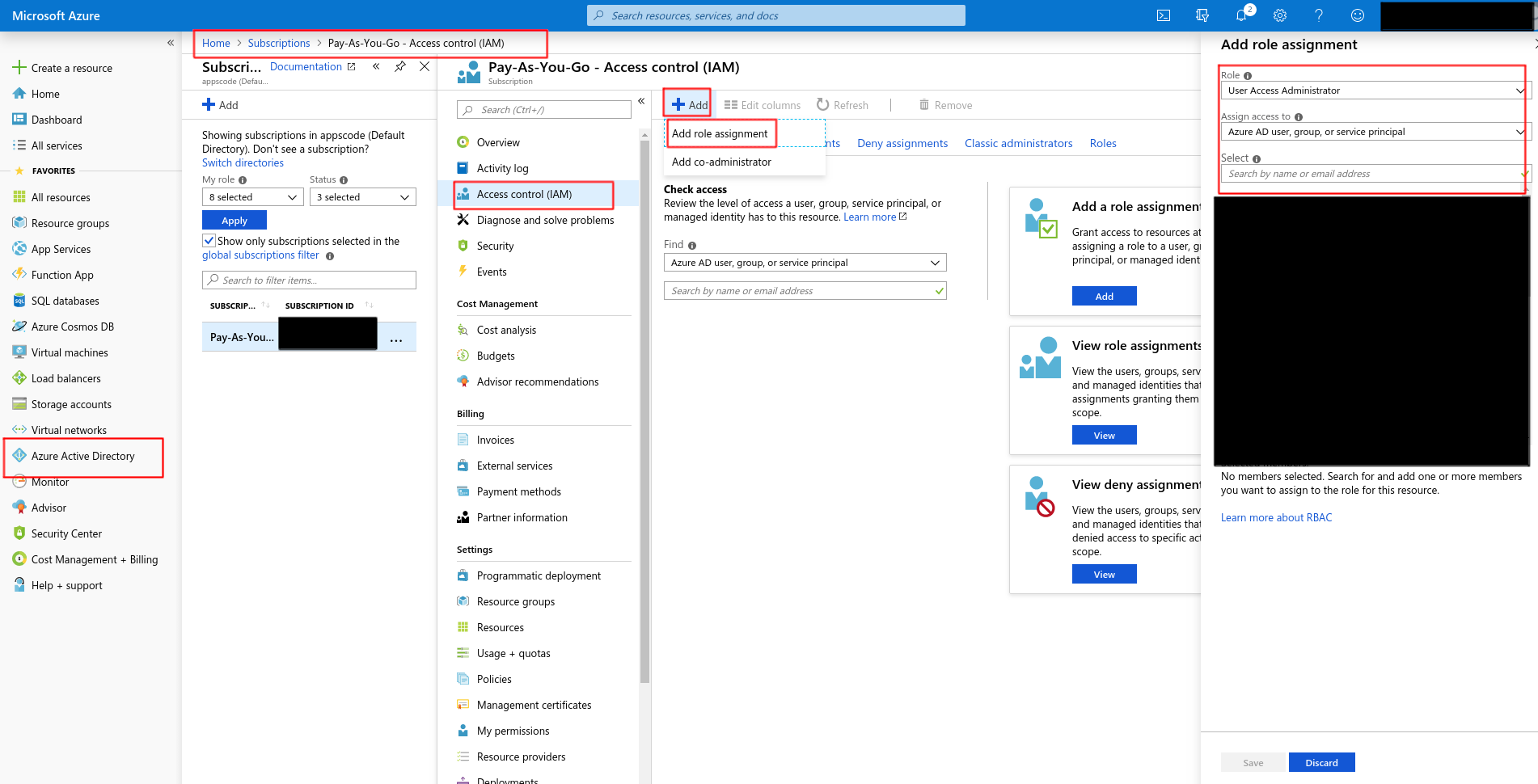
Click on Access control (IAM) and Add -> Add role assignment.
If you see this as Add role assignment (disabled) then have your portal administrator perform this step, otherwise ignore this.
Your administrator needs to go to the same page and add you as Owner or User Access Administrator
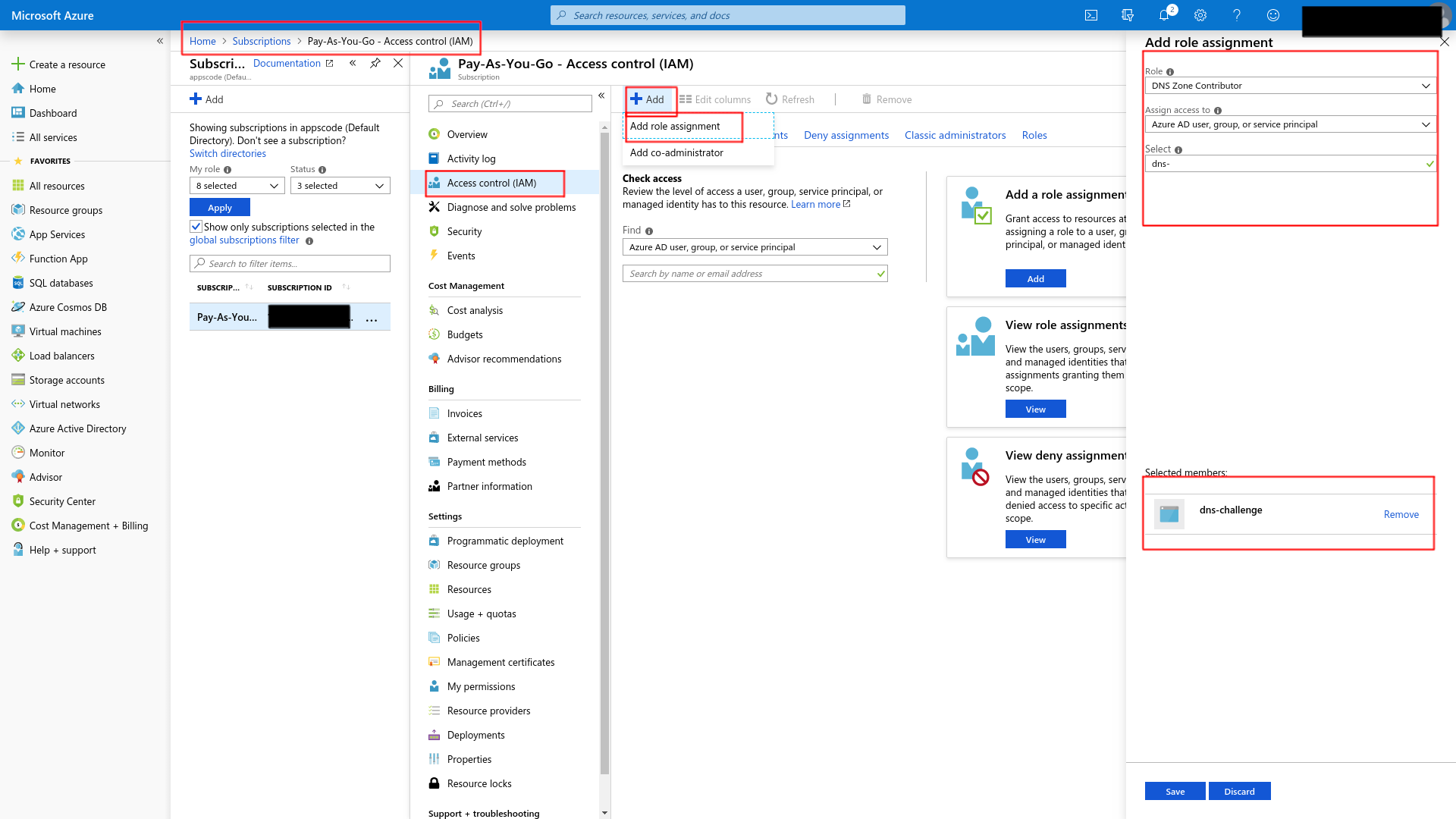
Now that you have access to this, go to Subscriptions -> Access control (IAM) -> Add and you should be able to Add role assignment. Add DNS Zone Contributor to dns-challenge (the app registration you created before)
Now create this issuer by applying issuer.yaml
apiVersion: cert-manager.io/v1
kind: Issuer
metadata:
name: letsencrypt-staging-dns
namespace: default
spec:
acme:
server: https://acme-staging-v02.api.letsencrypt.org/directory
email: example@kite.com
# Name of a secret used to store the ACME account private key
privateKeySecretRef:
name: example-issuer-account-key
solvers:
- dns01:
azureDNS:
# Service principal clientId (also called appId)
clientID: riu478u-486ij8-uiu487j-468rjg8
# A secretKeyRef to a service principal ClientSecret (password)
clientSecretSecretRef:
name: azuredns-secret
key: client-secret
# Azure subscription Id
subscriptionID: 45ji8t4-rgi4859-g845jg-9jjf9945r
# Azure AD tenant Id
tenantID: 348585ej-4358fdg8-f4588fg-45889fg
# ResourceGroup name where dns zone is provisioned
resourceGroupName: dev
hostedZoneName: appscode.info
2. Create Ingress
We are going to use a nginx server as the backend. To deploy nginx server, run the following commands:
kubectl run nginx --image=nginx
kubectl expose deployment nginx --name=web --port=80 --target-port=80
Now, Create ingress.yaml
apiVersion: networking.k8s.io/v1
kind: Ingress
metadata:
name: test-ingress-deploy-k8s-azure-dns
namespace: default
annotations:
kubernetes.io/ingress.class: voyager
certmanager.k8s.io/issuer: "letsencrypt-staging-dns"
certmanager.k8s.io/acme-challenge-type: dns01
spec:
tls:
- hosts:
- kiteci-azure-dns.appscode.info
secretName: kiteci-azure-dns-tls
rules:
- host: kiteci-azure-dns.appscode.info
http:
paths:
- backend:
service:
name: web
port:
number: 80
path: /
pathType: Prefix
Then take the EXTERNAL-IP from the corresponding service and add a A-record in Azure DNS:
kubectl get svc
NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE
voyager-test-ingress-deploy-k8s-azure-dns LoadBalancer 10.7.254.246 35.192.150.216 443:31233/TCP,80:32271/TCP 26h
3. Create Certificate
Then create this certificate.yaml
apiVersion: cert-manager.io/v1
kind: Certificate
metadata:
name: kiteci-azure-dns
namespace: default
spec:
secretName: kiteci-azure-dns-tls
issuerRef:
name: letsencrypt-staging-dns
dnsNames:
- kiteci-azure-dns.appscode.info
Now, List the certificates and describe that certificate and wait until you see Certificate issued successfully when you describe the certificate.
kubectl get certificates.certmanager.k8s.io --all-namespaces
Then visit kiteci-azure-dns.appscode.info from browser and check the certificate that it was issued from let’s encrypt. (For let’s encrypt staging environment, you will see that the certificate was issued by Fake LE Intermediate X1.)









